First Steps
Regular Maintenance
It's important to perform regular fridge maintenance before trying these fixes. Your appliance should last for at least 10-15 years before needing replacement, so keep it running well with these refrigerator maintenance tips.
Safety Note: Power Down the Fridge
Before removing and replacing or continuity testing electrical components, power down the fridge. This will prevent damage to the components and prevent you from being electrocuted. Still, some electrical components — like capacitors — will store their charge and should not be tampered with.
- If the fridge is pulled away from the wall, or if the power switch is easily accessible, remove the plug.
- Otherwise, find the fridge’s circuit breaker in your breaker box and turn the circuit off.
- Verify your fridge has lost power by opening the doors and seeing if the fridge lights turn on.
Safety Note: Sharp Sheet Metal
When working underneath the fridge, consider wearing gloves to avoid cuts from the sharp sheet metal. The sheet metal is the thin structural metal where components mount. While wearing gloves may make work more challenging, it’s worth protecting yourself.
Reset Power
When refrigerators experience temporary power outages, they may enter a safe mode. The safe mode protects the fridge's internal components from electrical overloading. You'll have to reset the power to your fridge.
- Unplug your refrigerator. If the plug is too hard to reach, switch the circuit breaker off.
- Wait 5 minutes before returning power to the fridge.
- Once power is back, open your freezer and push the light switch 3 times to trigger a cooling cycle.
- Monitor temperature over the next 24 hours.
Causes
The evaporator fan blows cold air around the freezer. Too much food or incorrectly placed food will block the vents and prevent proper temperature regulation. The refrigerator vents allow for airflow between the fridge and freezer compartments. The following tips may help your freezer maintain a safe temperature:
- Locate your evaporator fan and move frozen items further away.
- Unblock the vents. A rule of thumb for frost prevention is to stock enough food to fill the freezer while keeping an inch of space between the food and the walls.
A buildup of interior frost and ice can affect your unit's efficiency. If it's been a year or more since you last defrosted the freezer, perform a forced defrost or manual defrost.
- Unplug or power down your unit
- Unload the freezer and carefully remove the ice.
- Lay towels in the bottom of the machine, and then place bowls of hot water or a hairdryer/heat gun — carefully — in a position to melt the ice.
- Completely dry the freezer before powering back on.
If you have an auto-defrost unit, the accumulation of thick ice suggests some part of the defrost cycle has failed.
Door seals are gaskets for your fridge, and as they age and fall apart, cool air escapes through the cracks in door seals.
- Inspect your door seals, then clean or replace if necessary.
At the backside and bottom of your fridge are the condenser and its coils. The refrigerant passes through the coils which dissipate heat during the cooling cycle. As dust and debris pile onto the coils, the fridge becomes less efficient and must work hard to cool down.

- Pull your fridge out and inspect the coils.
- Your fridge may have an anti-tip bracket and can only be removed by pulling straight out from the wall.
- Clean dust off condenser coils and fan with a stiff brush and vacuum.
- Work carefully during this task and avoid bending or damaging the tubes.
The condenser fan draws air over the compressor and through the condenser coils. If the fan motor isn't working normally, then the fridge won't cool properly. It's normally located at the bottom of the fridge and blows air onto the condenser coils.

- Check the fan blade for physical obstructions
- Rotate the fan by hand. If it doesn't spin freely, replace the motor.
- If it spins freely, test the motor for continuity. Replace the condenser fan motor if the continuity test fails.
The evaporator fan draws air over the cooling coils and circulates this air within the fridge and freezer compartments. The evaporator fan should be running as long as the compressor motor is running. If your fridge only has one evaporator fan motor, it's located in the freezer compartment. When the fan fails, it won't circulate the cold air to the refrigerator. In this event, the freezer may still get cold while the refrigerator stays warm.

- Check the fan blade for physical obstructions.
- Note: The fan may not be running if it's iced or frozen. Defrost the freezer, and see if the fan spins freely.
- Rotate the fan by hand. If it doesn't spin freely, replace the motor.
- If it spins freely, test the motor for continuity. Replace the evaporator fan motor if the continuity test fails.
- An unusually noisy motor should be replaced as well.
Newer freezers may use brushless fans which are not easily taken apart or tested.
In very rare cases, the motor for the fan can end up spinning backwards. Yes, an A/C fan. The solution is to replace the motor.

- 5 minutesEasy
If the refrigerator still does not get cold enough, the temperature control thermostat (also called a bi-metal thermostat) might be faulty. The thermostat allows power to flow through to the compressor, evaporator fan, and condenser fan. If the cooling system fans and compressor are running, but the refrigerator or freezer is not cooling correctly, check for an airflow or defrost system problem.
- Continuity test the thermostat.
- Make sure it's cold from the fridge or sitting in ice water.
- Replace if its resistance value is outside of 0-1Ω.

- 5 minutesEasy
Another problem that prevents your fridge from getting cold enough is a faulty thermistor. The thermistor is a sensor that monitors the air temperature. It is connected to the control board. If the thermistor is defective, the refrigerator does not cool (or may cool continuously).
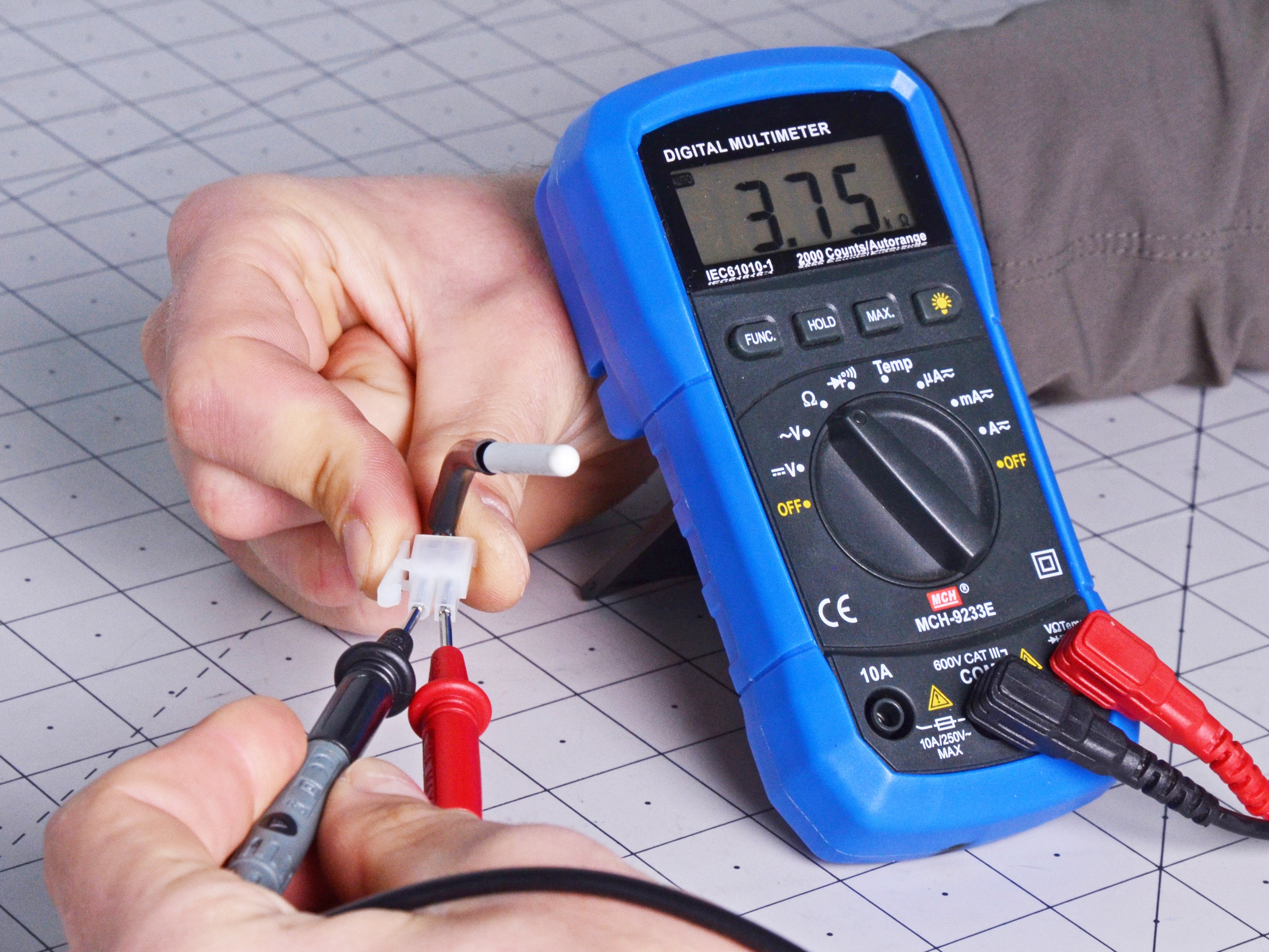

- Grab a multimeter and continuity test the thermistor. You can measure the thermistor if it is 46 degrees Fahrenheit (7 degrees Celsius) or colder. Place the thermistor tip into a cup of ice water and cool if you're above the target temperature.
- If the value isn't between 10—15kΩ, replace your temperature sensor.

- 5 minutesEasy
Sometimes if the refrigerator isn't cold enough, the compressor might be having difficulty starting up. The start capacitor serves as a battery to give the compressor a boost of power during startup. If the start capacitor is burned out —and smells burnt — the compressor might not be able to start and run as often as it should.

- Safely remove the capacitor and discharge with a discharge tool.
- On smaller capacitors, you can use a screwdriver to discharge. But be careful as capacitors increase in size.
- Test the start capacitor first with a capacitance meter; they don't fail often. If it's faulty, replace it.

- 2 - 15 minutesModerate
The overload relay is a protection device in the compressor circuit and is often combined with the start relay. You can find it plugged directly into the side of the compressor. If the fans are running and your compressor won’t start, or if you hear a clicking sound from the unit follow the troubleshooting below.
 |  |
- Check the overload relay for signs of overheating or arcing.
- This may be a hot module, burnt, or rattles when shaken.
- Check for continuity with a multimeter.
- Flip the unit over and test again. If there's no continuity, replace the unit.

- 5 minutesEasy
The start relay is a small device mounted to the side of the compressor. It provides power to the run winding, along with the start winding, for a split second at startup to help get the compressor going. If the start relay is defective, the compressor may run intermittently or not at all, and the refrigerator will not get cold enough. The start relay should be replaced if defective.
- Test Start Relay with a multimeter. View the video above and verify if your start relay is functioning.
- Replace the relay if it fails the testing or has a burnt odor. Depending on your start relay, you may have to test the start capacitor and overload relay first and use a process of elimination. If the other two components pass continuity tests, and your compressor isn't starting, try replacing your start relay.
The compressor — also called the condenser — is the workhorse of your fridge. By pressurizing the refrigerant, the evaporator is able to create cold air. If the compressor is very noisy when you start it up, it may have been damaged in transit, or you could just have a faulty compressor.
If the overload relay, start relay, and start capacitor pass continuity testing, then you may have a defective compressor.
- Test the compressor for continuity by following the video above.
- Resistance values vary based on the compressor.
- Values outside of the range or a short to ground will mean replacing the compressor, which is a costly repair.
- If your fridge is more than a few years old, you may be better off replacing the fridge instead of the compressor.
Excessive vibration and aging connections in the pressurized refrigerant loop can cause an environmentally harmful release of refrigerant. There are a few ways you can check if this is the case.
Is the compressor continually running to keep the fridge cool? A low refrigerant pressure results in cooling problems such as the freezer being too warm. If the freezer's coils are not frosting over completely this also suggests a leak or a blockage in the cooling system.
- Inspect for oily residues on condenser coils and on or around the compressor. The refrigerant is mixed with oil which lubricates the compressor. Oil suggests that there's a refrigerant leak.
A blockage can be caused by tilting or transporting a fridge on its side. The lubricating oil at the bottom of the compressor can enter the refrigerant lines and cause the compressor to burn out. A blockage in the system can cause ice build-up on the other side of the restriction in the refrigerant flow path.
- An appliance technician can measure the low and high side pressures of the sealed refrigerant system. The pressures will indicate if the amount of refrigerant is correct and also if there are any restrictions in the sealed system.
In either case, replacing the compressor is an expensive fix, not DIY, and may be worth replacing the fridge entirely. Try every other fix first. Good luck.
Finally, if the refrigerator won’t get cold enough, the main control board might be defective. This is not common. Check the defrost system, cooling fans, and cooling controls first.
- If all other systems seem fine, replace the main control board.
You're seeing solutions for Refrigerator. Select your model to find parts for your device.